Ten Main Causes of Climate Change
Ten Main Causes of Climate Change: The Main Causes of Climate Change. Major Causes of Climate Change. Natural and Human Causes of Climate Change. What are the Main Causes of Climate Change PDF?
Climate Change
Climate change means a change in the atmosphere of specific areas for a long time. It also refers to the new condition of the weather, including drought, temperature, rain, earthquake, snowfall, and so more. Climate change brings different weather to the Planet different than in previous years. The climate of the Earth has changed in the current decades. It is related to global warming, which is a much-talked topic globally. Global warming denotes increasing the temperature of the Earth. However, climate change mentions the rising temperature and reduces the Earth’s temperature.
The temperature on the Planet has risen dramatically in the last 100 years. For instance, the Planet is 2 degrees Celsius warmer than last century. However, the Earth’s temperature has never been constant; instead, it evolves occasionally. The last five years were the warmest year in the current age. The top country leaders, including the prime ministers in America, Canada, and Australia aware of the climate change topic. World leaders and scientists have devised a vision to control the Planet’s temperature.
Causes of Climate Change
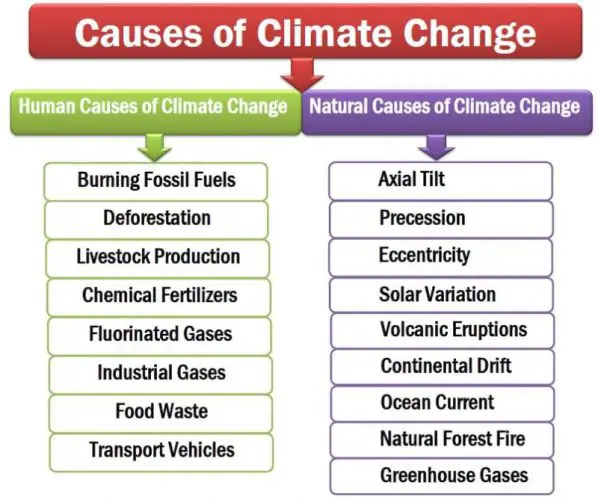
The two main causes of climate change are human and natural causes of climate change. Natural causes refer to the physical factors that contribute to the change of the atmosphere on the Earth. On the other hand, human causes mean artificial factors and people’s activities that change to climate on the Earth. Based on the studies, the author has outlined nine major natural and eight human causes of climate change on the Planet.
Ten Main Causes of Climate Change
The 10 Causes of Climate Change are:
- Solar Activities
- Volcanic Eruptions
- Axial Tilt
- Precession
- Eccentricity
- Continental Drift by Plate Tectonics
- Ocean Current
- Natural Forest Fire
- Natural Greenhouse Gases
- Human Causes of Climate Change
Natural Cause of Climate Change
Natural causes refer to the actual elements and actions that contribute to changing the atmosphere of the Earth. It is also known as the physical cause of climate change. Natural factors occur naturally from the natural cycle of the Planet. The most common physical causes are the Milankovitch cycle, ocean, gravity, forest fire, solar activities, volcano, and greenhouse gases(GHG). People can’t control these factors; therefore, these are known as natural causes. Some factors contribute to increasing temperature on the Planet; on the other hand, other factors trigger to reduce. These natural causes stimulate change to the condition of the Planet instantly and slowly.
The nine physical causes of climate change are Solar Variation, Volcanic Eruptions, Axial Tilt, Precession, Eccentricity, Continental Drift, Ocean currents, Natural Forest Fires, and Natural Greenhouse Gases.
1. Solar Activities
Solar activities mean releasing various types of radiation from the sun from time to time. It includes sunspots, solar flares, and solar radiation. For example, sunspots release more solar radiation than the regular portion of the sun, making the planet warmer. So, the sun’s heat depends on the solar activities driven by the sunspots. Recently scientists have identified many sunspots on the sun’s outer layer that emit a larger number of solar radiation. However, the temperature in the sunspot is lower than the natural part of the sun. It seems like a black hole that gets visible for the magnetic cycle. Sunspots occur from the storm on the surface. It is the most crucial factor in the sun that emits solar flares.
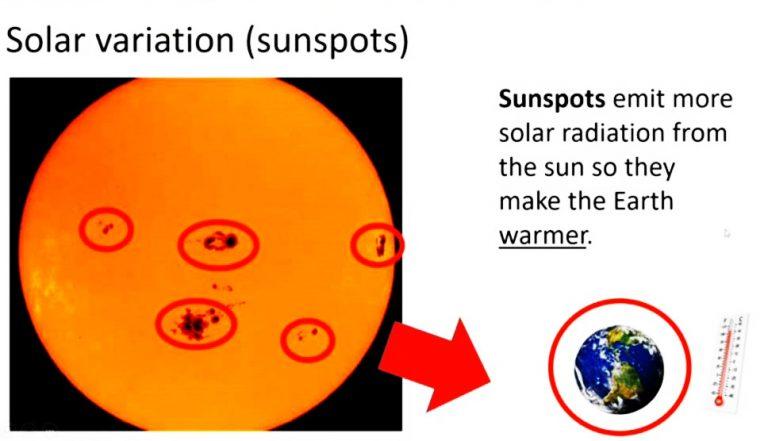
The sunspot’s temperature is around 3,800 degrees Kelvin, and the sun’s average temperature is 5,800 degrees, Kelvin. So, the sunspot’s temperature is lower than another part of the sun. Sunspots emit many ultraviolet rays that hit the Planet’s surface and increase the temperature. It takes 11 years to reach the sunspots on a peak known as the solar maximum. The solar minimum of the solar cycle occurs when a small number of sunspots are visible. In recent decades, the Planet’s temperature has risen 0.1 degrees Celsius due to solar maximum. It makes the sun brighter and the Planet warmer.
2. Volcanic Eruptions
Volcanic eruption is a natural hazard that occurs naturally. It releases a massive number of dust, magma, and gases that affect the environment. The most adverse impact of the volcanic eruption is destroying the ecosystems. Many people can die from the eruption who stay near to the place. Additionally, it raises around 1100 degrees Celsius temperature of the surrounding area. The lava can set fire to the forest which causes forest fires. Volcanic eruption destroys animal diversity and the ecosystem when it occurs in the ocean. The dust and gases emitted from the volcanic eruption make a dark ash cloud in the atmosphere. This ash cloud works like a sheet that reflects the sun’s radiation. Solar radiation cannot enter the Planet due to the ash cloud in the sky. Therefore, the ground place gets colder than the average temperature.
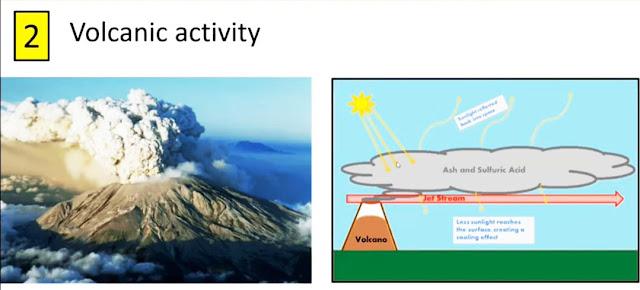
Many people believe that volcano eruptions raise the Planet’s temperature that is not true. The boiling lava emitted from the volcano increases the surrounding temperature for a short time. However, the ash cloud reflects the solar radiation that makes the surrounding area colder for a long time.
3. Axial Tilt
The Milankovitch Cycle describes the entire process of the planet’s orbitals the sun. The Planet needs 365 days to move around the sun. At the same time, the sun needs only 24 fours to rotate on its axis.
Axial tilt is the angle of the Planet that occurs during rotation. It relates to the angle within the orbital and perpendicular plane. Axial tilt is also called obliquity. The axial tilt or obliquity is responsible for the various seasons on the Planet. The Planet is 23.5 degrees tilted from its orbital plane. Usually, the obliquity differs from a minimum of 22.1 degrees and 24.5 degrees during rotation. The season gets extended when the axial tilt is maximum, and the season gets shorter when the axial tilt is minimum. The Planet consumes more solar radiation when it rotates with maximum tilted towards the sun. In contrast, the Planet receives less heat from the sun when it tilts on the opposite side of the sun.
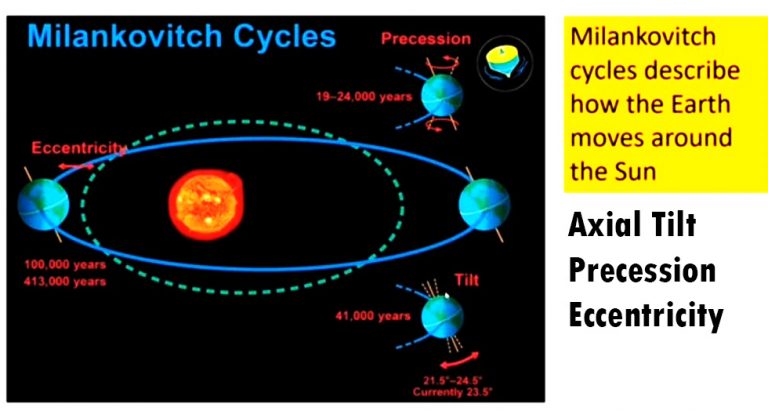
The cycle takes 41,000 years to get back to the ice age; people will see the ice age again after 41,000 years. The Planet is 23.5 degrees tilted towards the sun; therefore, it receives more heat from the sun. It is the reason for extended summer and winter on the Planet.
4. Precession
Precession is the transition of rotational axis adjustment for the gravity power. It relates to the action of the gyroscope power. It takes around 26,000 years to complete the entire cycle. The Planet wobbles towards the sun or opposite the sun after this period which contributes to the change in the climate. The Planet gets more solar radiation when it leans toward the sun for precession. On the other hand, it gets less heat when tilted opposite the sun. So, precession is the natural cause of changing the atmosphere on the Planet.
5. Eccentricity
Eccentricity refers to the Planet’s position while moving around the sun; therefore, it is called orbital eccentricity. The Planet takes 365 days to orbit the sun completely. The Planet does not follow the same path to move as the sun. We know that the planet moves around the sun in a circle that is not true. The Planet does not move the sun in the same way. Sometimes, it moves the sun elliptical way. So, it measures the deviation of the circular path of the Planet. Orbital eccentricity is included the deviation of the circular and elliptical way of the Planet’s movement around the sun. The variation of the Earth’s movement around the sun controls the solar radiation received from the sun. The deviation path sets the distance between the Planet and the sun.
The summer season is longer than the winter due to the orbital path variation- for example, it is around five days longer than the winter season. The Planet is located approximately 94.5 million miles away from the sun during the summer season. So, the Planet receives more solar radiation from the sun when it locates the farthest distance. It receives more heat, not for distance but the position of the Planet. In contrast, the Planet locates around 91.4 million miles far from the sun in the winter season. The Planet moves around the sun in a short distance during the winter season. The cycle takes around 100,000 years to complete the round. Now the position of the Planet and sun is not circular rather, it is elliptical in shape with an eccentricity e ≈ 0.0167.
6. Continental Drift by Plate Tectonics
Continental drift means the movement of the Planet’s plate tectonic called a change in the Planet’s crust. The Planet has seven continents, and the position of these continents is not constant. The research has shown that few continental drifts are moving slowly. The process of movement is prolonged. The movement motion is approximately 0.5 to 10 cm annually.
Hence, the movement of continental drift causes changes in the atmosphere on the Planet. It has both positive and negative consequences on the Planet. The continent is set on the Planet’s crust, and each continent is separated from another. The tectonic crust differs into two types: less dense and denser crust. These tectonic crusts move slowly and independently. The movement of these crusts is responsible for earthquakes, volcanoes, and tsunamis. Few factors provide evidence of the Planet’s crust movement, such as crust collision, subduction, spreading, and movement fault. The plate tectonic collision is the main reason for the earthquakes. Recently, a study showed that the Himalayan mountain height has extended due to the clash between the Indian and Eurasian plates.
The collision between plates is also responsible for volcanic eruptions. It emits lava that is made from molten rock. So, continental drift is responsible for changing the atmosphere on the Planet.
7. Ocean Current
The ocean current refers to the continuous movement of the ocean waters. It is one of the crucial physical causes of changing the environment. The ocean current is formed from the gravitation power between the sun and moon, winds, and the Planet’s axial rotation. The ocean occupies around 75% of the Planet’s area, absorbing most solar radiation from the sun. Solar radiation evaporates the ocean water and generates vapor gases(H20). Although the land receives some solar radiation, it returns some heat to space. The ocean release very little heat compared to the land areas. Solar radiation evaporates the water and creates the ocean current. The evaporation process raises the temperature in the surrounding areas on Planet. However, it makes rains through the evaporation cycle that reduces the temperature and humidity.
The ocean current melts the northern part’s ice, increasing the sea level. It is responsible for melting the ice in raising the sea level continuously. The Planet’s weather gets changes rapidly if there are no ocean currents. It warms the Planet.
8. Natural Forest Fire
Forest fires mean burning a forest for natural and human activities. Wild forest fire is the burning of a forest due to natural causes such s drought and lightning. It is a physical or biological cause of environmental change. Fires always create smoke, dust, greenhouse gases, and heat. These elements undoubtedly raise the temperature of the surrounding areas.
The most common types of forest fires are natural and human forest fires. Wild forest fires occur naturally without humans’ activities. On the other hand, human forest fires mean set the fire by people intentionally or unintentionally. Forest fires can burn millions of plants, animals, insects, and birds. Its impacts the ecosystem and diversity extremely. Studies have shown that natural forest fires are only 18 percent and artificial forest fires occupy 82 percent.
The warm temperature during the summer season triggers to set fires in the forest. It engulfs the entire forest within a short time. Although lightning and drought are responsible for setting fire in the woods, the wind soon spread the fires.
Forest fires can make a green forest into a dark desert. Forest fires release many greenhouse gases, for example, carbon dioxide (Co2), methane (Ch4), and ashes. The greenhouse gas, especially carbon dioxide, traps the heat in space that, increases the temperature of the Planet. Additionally, it spoils the soil nutrient and creates methane gases that raise the planet’s temperature.
9. Natural Greenhouse Gases
There are two types of greenhouse gases: natural gas created naturally and greenhouse gases produced by human activities. Natural greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO2), water vapor (H2O), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and ozone (O3). These gases increase the Planet’s temperature by trapping heat in the temperature. The volcanic eruption, forest fires, and ocean currents generate carbon dioxide and water vapor, greenhouse gases. These gases can be created without human involvement; therefore, they are natural greenhouse gases.
These greenhouse gases let solar radiation enter the Planet easily; however, they trap the heat in space without letting them go back. So, the greenhouse gases stimulate to raise the temperature of the Planet.
There are two effects of climate change on the Planet: the direct and indirect impacts of climate change.
10. Human Causes of Climate Change
1. Direct Impact of Climate Change
Climate change increases the maximum temperatures and reduces the minimum temperature level. The prolonged maximum temperature melts the ice in the northern part and increases the sea level. Additionally, It raises the ocean’s temperature and brings a humid atmosphere. The higher temperature of the ocean evaporates water into vapor and makes heavy rains.
2. Indirect Impact of Climate Change
Climate change creates a water crisis, and groundwater levels are decreasing daily. In many developing countries, people suffer from water crises. These countries experience drought and flood every year. After all, it increases hunger and diseases among poor people. Climate change is directly responsible for to loss of diversity and ecosystem crisis. The contamination of the CO₂ and HCO3 concentrations in the water creates acid rain that is bad for people’s health.
Climate change is also responsible for floods, erosion, landslides, and salinization. The sea level is increasing day by day due to global warming.
Conclusion
The author has represented the leading human causes of climate change and natural causes that contribute to changing the global atmosphere. People cannot prevent the biological causes of climate change. However, people can prevent human causes of climate change by protecting the environment.














I appreciate the simple but clear discussion of the natural causes and the human causes of Climate Change. Thank you.